Angle type globe valves are essential components in industrial systems, specifically designed to regulate the flow of fluids effectively. Used in a variety of sectors, including oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing, these valves offer precise control and are known for their robust performance under challenging conditions. This guide will provide an in-depth understanding of angle type globe valves, covering their design, applications, benefits, and tips on how to select the right valve for your needs.
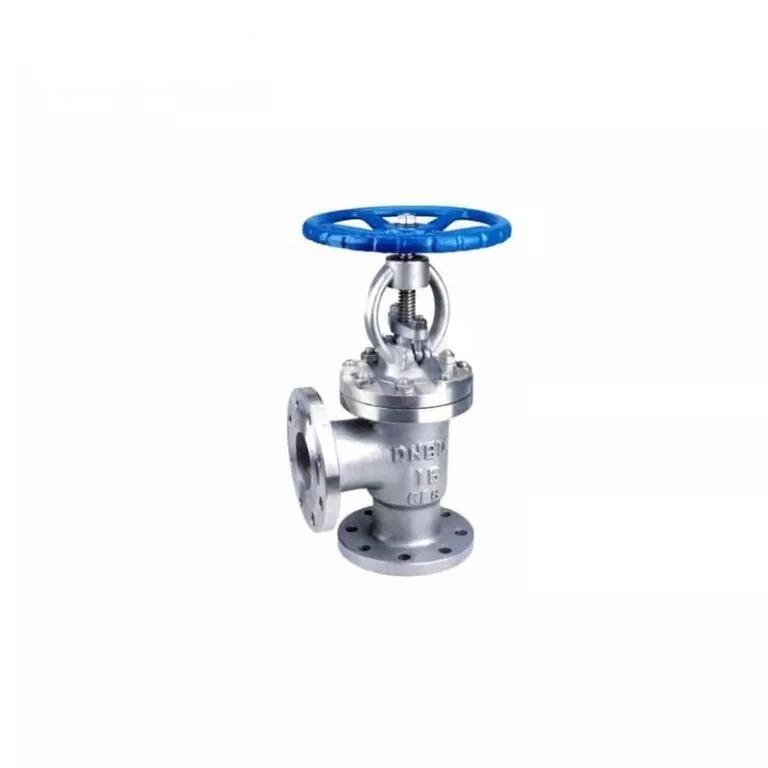

Introduction to Angle Globe Valves
An angle globe valve is a specialized version of the standard globe valve, designed with an angled configuration that allows for efficient flow control while minimizing pressure drop. Unlike traditional globe valves that align the inlet and outlet ports in a straight line, angle type globe valves have the outlet port positioned at a 90-degree angle relative to the inlet. This unique design makes them particularly effective in applications that require a change in flow direction, offering both practical and performance-related advantages.
Angle type globe valves are commonly used in industries where precise flow control and durability are crucial. They are ideal for systems that need frequent flow regulation, such as steam lines, cooling water systems, and other critical service conditions that require reliable throttling and minimal leakage.
How Do Angle Globe Valves Work

Angle Globe Valve Diagram
Based on the image above, an angle globe valve operates as follows:
Flow Control
The angle globe valve has a design where the fluid enters at an angle (typically 90 degrees), allowing it to change direction as it flows through the valve. This is achieved through the angled body design, which reduces the space required for installation and minimizes pressure drop across the valve.
Operation Mechanism
- The valve has a handwheel (labeled as part 16), which is turned to operate the valve.
- When the handwheel is rotated, it moves the stem (labeled as part 9) up or down. This stem movement is transmitted to the disc (labeled as part 5).
- When the handwheel is rotated clockwise, the stem pushes the disc down toward the seat (labeled as part 1), closing the valve. This prevents fluid from passing through.
- When the handwheel is rotated counterclockwise, the stem lifts the disc away from the seat, allowing fluid to flow through the valve.
Sealing
The gasket (part 06) and packing gland (part 08) are used to create a seal around the stem and prevent leaks. The packing gland, located near the top of the valve body, helps seal the area where the stem exits the body to ensure no leakage around the moving parts.
Advantages
Angle type globe valves offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice for many industrial applications:
| Feature | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Design Efficiency and Space Optimization | The 90-degree angled configuration eliminates the need for additional pipe fittings, saving installation space and reducing pressure drop for enhanced system performance. |
| Superior Flow Control and Throttling Capabilities | Allows precise regulation of fluid flow due to the disc’s perpendicular movement to the seat, ideal for applications requiring fine throttling and flow control. |
| Enhanced Sealing and Leak Prevention | Provides a tight disc-to-seat alignment for minimal leakage, ensuring fluid retention and system pressure stability, crucial in high-value or hazardous fluid applications. |
| Durability and Maintenance Considerations | Made from corrosion- and wear-resistant materials, angle globe valves are durable and have accessible components for easy maintenance, reducing downtime and overall maintenance costs. |
| Versatility Across Applications | Suitable for a wide range of applications, including chemical processing, water treatment, and HVAC systems, due to their ability to handle various fluids, pressures, and temperatures. |
Applications
Angle type globe valves are versatile and used across various industries for numerous applications. Some of the most common sectors where these valves are employed include:
- Oil and Gas Industry: In oil and gas production facilities, angle type globe valves are used for regulating the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and steam. Their ability to handle high-pressure systems and provide accurate control makes them an excellent choice.
- Power Plants: In power generation, these valves are often used in steam and water systems for cooling, heating, and controlling fluid flows. Their robustness ensures reliable performance under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, which is critical in power plants.
- Chemical Processing: The chemical industry often requires valves that can precisely regulate the flow of aggressive chemicals. Angle type globe valves, with their ability to provide accurate flow control and resistance to corrosive substances, are widely used in these environments.
- Water Treatment: Angle type globe valves are also used in water treatment facilities to control the flow of water through different stages of treatment, including filtration and chemical dosing.
Angle Globe Valve Symbol
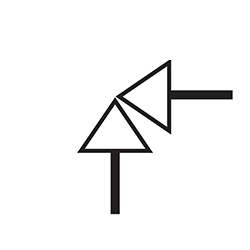
The angle globe valve, a variation of the standard globe valve, is distinctively designed with inlet and outlet ports arranged at a 90-degree angle. This configuration is especially useful in systems where space is limited or when specific directional changes are necessary. In P&IDs, this valve is represented by two triangles meeting at a right angle to form an ‘L’ shape. At their intersection, a solid black circle signifies the valve’s disc, clearly illustrating the valve’s structure and purpose. This symbol allows for quick recognition and a straightforward understanding of the valve’s function in complex systems.
How to Select the Right Angle Globe Valve
Selecting the appropriate angle-type globe valve is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in fluid control systems. This process involves a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors:
Application Requirements
- Flow Control Needs: Determine whether the system requires precise throttling or simple on/off control. Angle-type globe valves are particularly effective for applications necessitating accurate flow regulation due to their design, which allows for fine adjustments.
- System Pressure and Temperature: Assess the operating pressure and temperature ranges. Ensure the valve’s pressure rating and material composition can withstand these conditions without compromising integrity.
Material Compatibility
- Corrosive Media: For systems handling corrosive fluids, select valves constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or specialized alloys to prevent degradation.
- Temperature Extremes: In high-temperature applications, materials like stainless steel or high-temperature alloys are preferable due to their ability to maintain structural integrity under thermal stress.
Valve Design and Configuration
- Flow Direction and Piping Layout: The angle design facilitates a 90-degree change in flow direction, which can simplify piping layouts and reduce the need for additional fittings. This is advantageous in systems where space is constrained or where minimizing pressure drop is essential.
- Disc and Seat Design: Consider the type of disc (e.g., plug, ball, or composition) and seat configuration. These components influence the valve’s sealing capability and suitability for throttling applications.
Actuation Mechanism
- Manual vs. Automated Operation: Decide between manual handwheel operation and automated actuation (electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic). Automated valves are beneficial for remote control and integration into complex control systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Reliability
- Ease of Maintenance: Opt for valves with designs that allow straightforward access to internal components for inspection and repair. Features like bolted bonnets can facilitate maintenance procedures.
- Durability: Evaluate the valve’s construction quality and the manufacturer’s reputation to ensure long-term reliability and minimal downtime.
Compliance and Standards
- Industry Standards: Ensure the valve complies with relevant industry standards and certifications, such as ANSI, API, or ISO. Compliance guarantees that the valve meets established safety and performance criteria.
- Regulatory Requirements: Verify that the valve adheres to any specific regulatory requirements pertinent to the application, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing, where stringent standards are enforced.
By meticulously considering these factors, engineers and system designers can select an angle-type globe valve that aligns with their specific operational needs, ensuring efficient and reliable fluid control within their systems.
Maintenance Tips
To ensure longevity and reliability, proper maintenance of angle type globe valves is essential:
- Regular Inspection: Schedule regular inspections to check for any signs of wear or damage, particularly on the sealing surfaces.
- Lubricate the Stem: Regularly lubricate the valve stem to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear on the threads.
- Check for Leaks: Periodically check the valve for leaks. Addressing small leaks early can prevent larger issues and extend the valve’s life.
- Replace Worn Components: Over time, components like the disk or seat may wear out. Replacing these parts promptly ensures the valve maintains its performance.
Conclusion
Angle type globe valves are an essential part of many industrial fluid control systems, offering precise control, durability, and efficiency. Their unique design and ability to handle challenging operating conditions make them an excellent choice for industries like oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. When selecting an angle type globe valve, it is essential to consider factors such as material compatibility, pressure and temperature ratings, and flow requirements. Proper maintenance will ensure that these valves continue to perform reliably for years to come.


